Using fNIRS in clinical applications
Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) can measure relative concentration changes in oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin, which reflect local brain activity. fNIRS can be used in a variety of application areas to study the brain in different conditions and experiments. Due to its technical advantages, fNIRS is increasingly applied in clinical research to assess nthe eural activity of patients in various fields.
Why use fNIRS in clinical applications?
To perform research in medical applications, comfort, safety, and reliability are crucial. Especially when compared to other neuroimaging modalities such as fMRI, fNIRS comes with various advantages, making it a suitable technique for use in clinical research.
Non-invasiveness: fNIRS can assess neural activity non-invasively and safely.
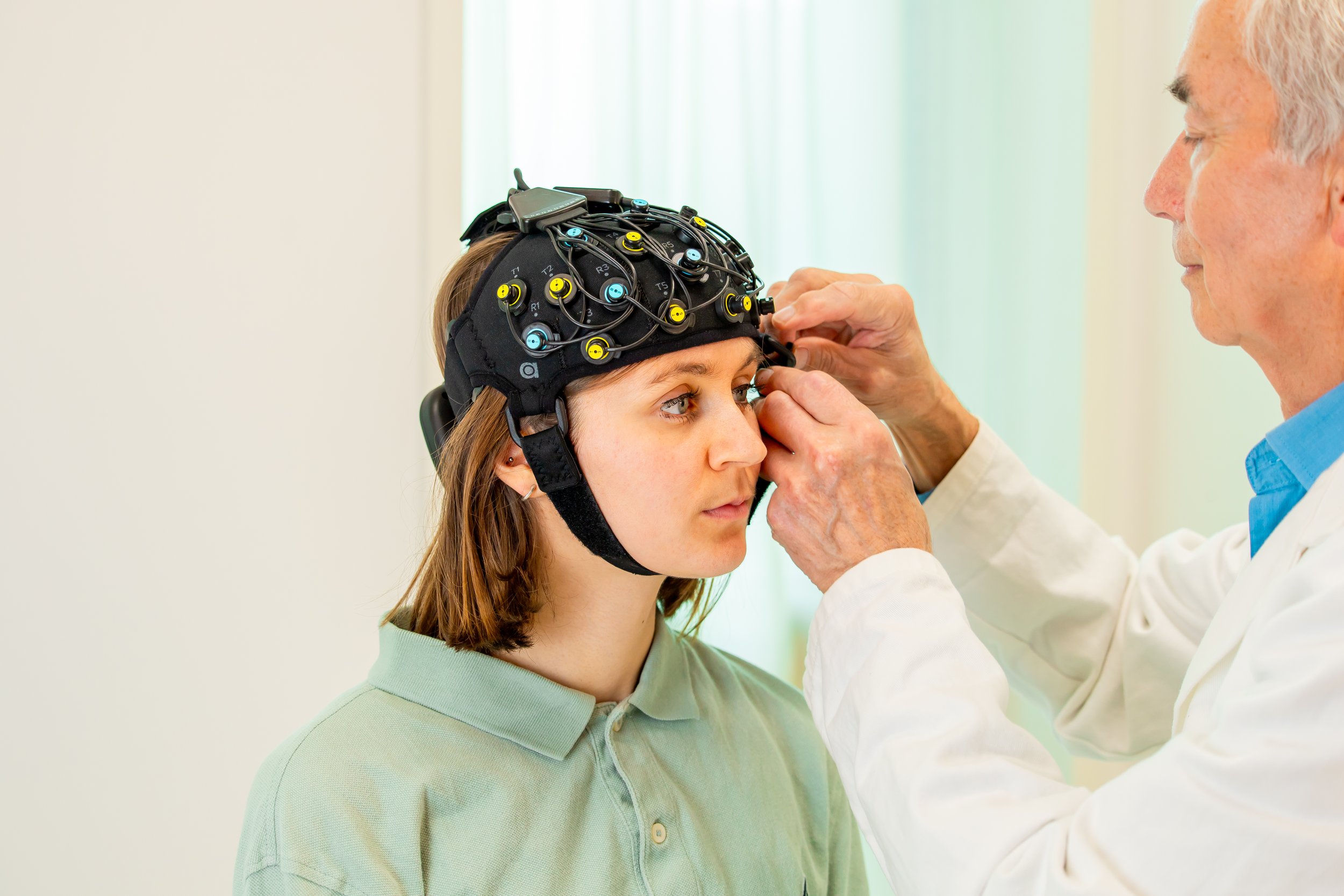
Fast and easy usage: Compared to other modalities, fNIRS can be set up and applied fast and relatively easily. This can reduce application time for both the patient and the researcher.
Freedom: fNIRS can be completely portable and wireless, allowing for measurements in every setting, for instance, at bedside, or even during movement or exercise performance, without being limited to a scanner. This allows for enhanced freedom for clinicians and patients and increases application possibilities.
Reliability: fNIRS is relatively insensitive to motion artifacts in comparison to other imaging techniques, which can help achieve a reliable signal. This enables patients to move during measurements, without the requirement to sit completely still.
Comfort: fNIRS is lightweight, flexible, and wearable. Hence, it enables shorter and longer measurements, still offering comfort for patients. This makes it a suitable tool to measure brain activity also in sensitive subjects, such as infants or the elderly.
Due to these technical features and resulting advantages, fNIRS can be safely and reliably applied in patients of all ages, genders, and origins in various settings and applications.
In which clinical fields can fNIRS be used?
Alternation of brain activity can play a role in the clinical population suffering from a variety of diseases/disorders in different medical fields. fNIRS offers the possibility to assess neural activity, and hence it can be used to study the brain in various application areas and diseases that can affect the brain. fNIRS finds, for instance, applications in psychiatry, neurology, rehabilitation, geriatrics, or neonatology/pediatrics, but is not limited to that.
For which purposes can fNIRS be applied in clinical research?
Measuring brain activity alternations and the detection of diseases
Several disorders can affect the brain and its neural function. fNIRS has previously been used to assess alterations in brain activity in patients with various disorders compared to healthy subjects. Evaluating differences in brain activity between clinical and healthy subjects gives insight into the mechanisms of diseases, points out possible therapeutic strategies, and shows diagnostic potential. Previous studies assessed the use of fNIRS as an adjunct detection tool to identify diseased populations in, for instance, psychiatric (e.g., depression, schizophrenia, ADHD) and neurological (e.g,. mild cognitive impairment) patients.
Study examples: Guevara et al. investigated the use of fNIRS and machine learning to detect Parkinson’s Disease.
Yi et al. performed a study to assess the potential of combined fNIRS-EEG and vector machine learning for the automatic diagnosis of depression.
Assessing the effect of treatment strategies
When introducing new treatment or therapy strategies for a clinical population, it is crucial to investigate, if they lead to a positive effect or improvement for patients, also on a neural level. fNIRS was previously applied to assess the effects of treatment, such as non-invasive brain stimulation (tDCS, TMS), physical rehabilitation programs, or medicines/supplements, by measuring and comparing brain activity in local regions before, during, and after intervention for patients suffering of different diseases.
Study examples:Beretta et al. assessed whether transcranial electrical stimulation can improve postural response in Parkinson’s patients
Sun et al. examined the effects of game-based high-intensity interval training on, for instance, executive function in children with ADHD
MediBrite — Portable Medical NIRS device
The MediBrite is the first European portable medical NIRS device that is CE certified according to MDR (EU) 2017/745. The MediBrite is completely portable, and lightweight, which enables free movement and comfortable measurements of brain activity using fNIRS. The device includes superior features to ensure high and reliable signal quality, but is still focusses on ease of use and quick application. Taken together, the MediBrite is the perfect fit for clinical research in various application areas, to measure neural activity from subjects of any age, gender, and race.
In this webinar, Dr. Edgar Guevara from CONACYT-Universidad Autonoma de San Luis Potosi explains how fNIRS can be used to measure brain activity in patients with Parkinson's Research. Presenting his findings on differences in brain activity of healthy and diseased subjects, as well as the potential detection of PD using fNIRS and machine learning, he demonstrates the application of fNIRS in clinical research.
Clinical NIRS made easy
Related case studies
More insights on our fNIRS devices
Are you interested in learning more about the MediBrite? Request a free 1-on-1 online demo to see our devices and our software!
Artinis Medical Systems
Einsteinweg 17
6662 PW Elst
The Netherlands
+31 481350980
Contact us
We’re here to help. We are open to any questions or comments, and we do our best to respond to you as soon as possible.








To provide professional intensive care specifically fit to cure COVID-19, hospitals need the appropriate space and equipment. Health care professionals have been working with limited resources in extreme environments but knowledge and experience is rapidly expanding. Several institutes have been implementing NIRS to study the endothelial and microvascular dysfunction to support the development of targeted and individualized therapies.