The power of portability — Using fNIRS in Naturalistic Settings
Conducting neuroscience studies in real-world environments is becoming increasingly important, as it can give novel and relevant insights into human behavior and neural mechanisms in daily life. Compared to other neuroimaging techniques, fNIRS comes with technical advantages such as portability, ease of use, and insensitivity to motion artifacts for perfect use in naturalistic settings.
In this post, we discuss different application areas of fNIRS in naturalistic settings, highlight study examples per category, and explain what solutions we can offer to promote fNIRS applications in real-world environments.
Setting #1
Investigating education and neural development
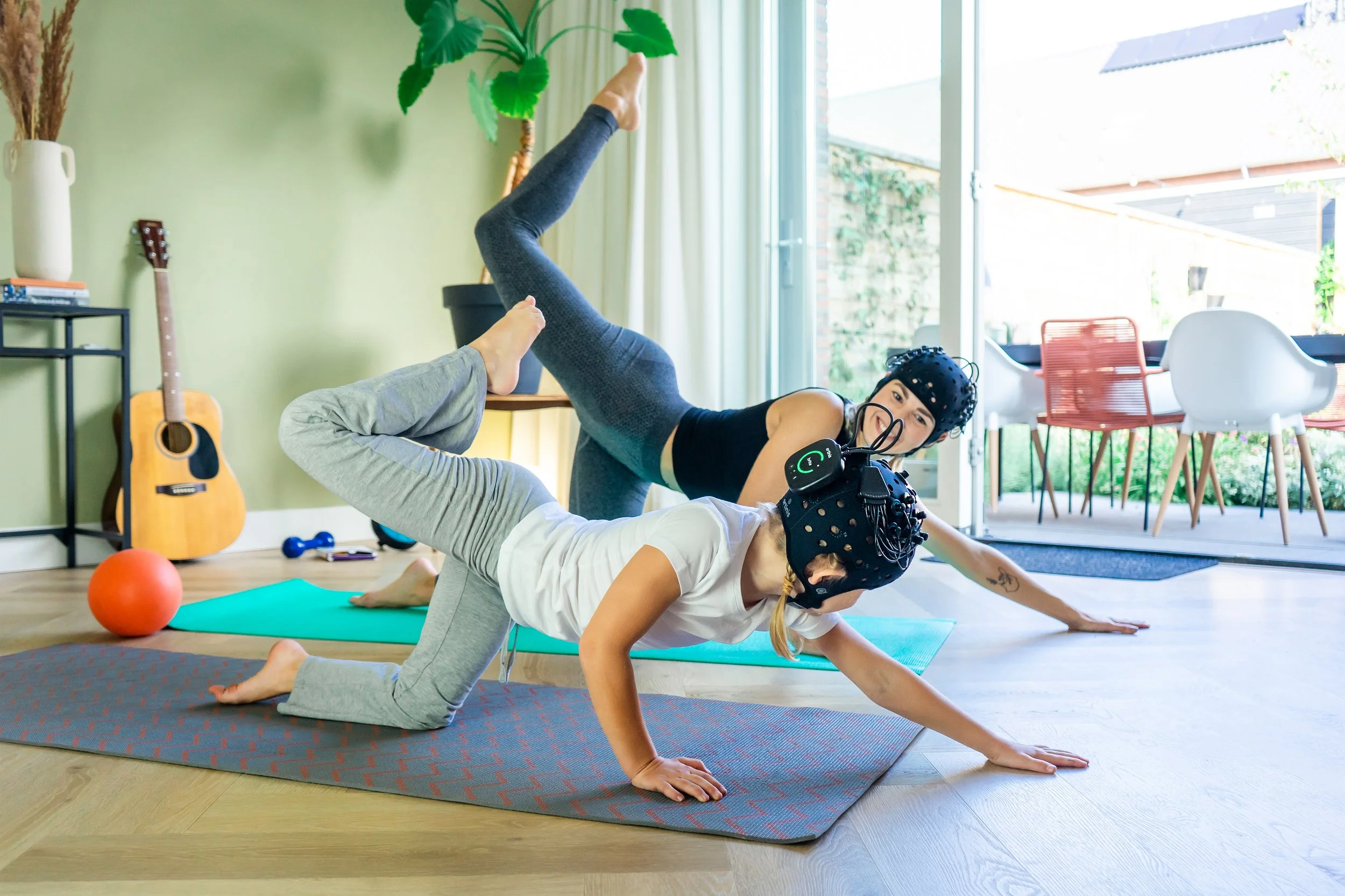
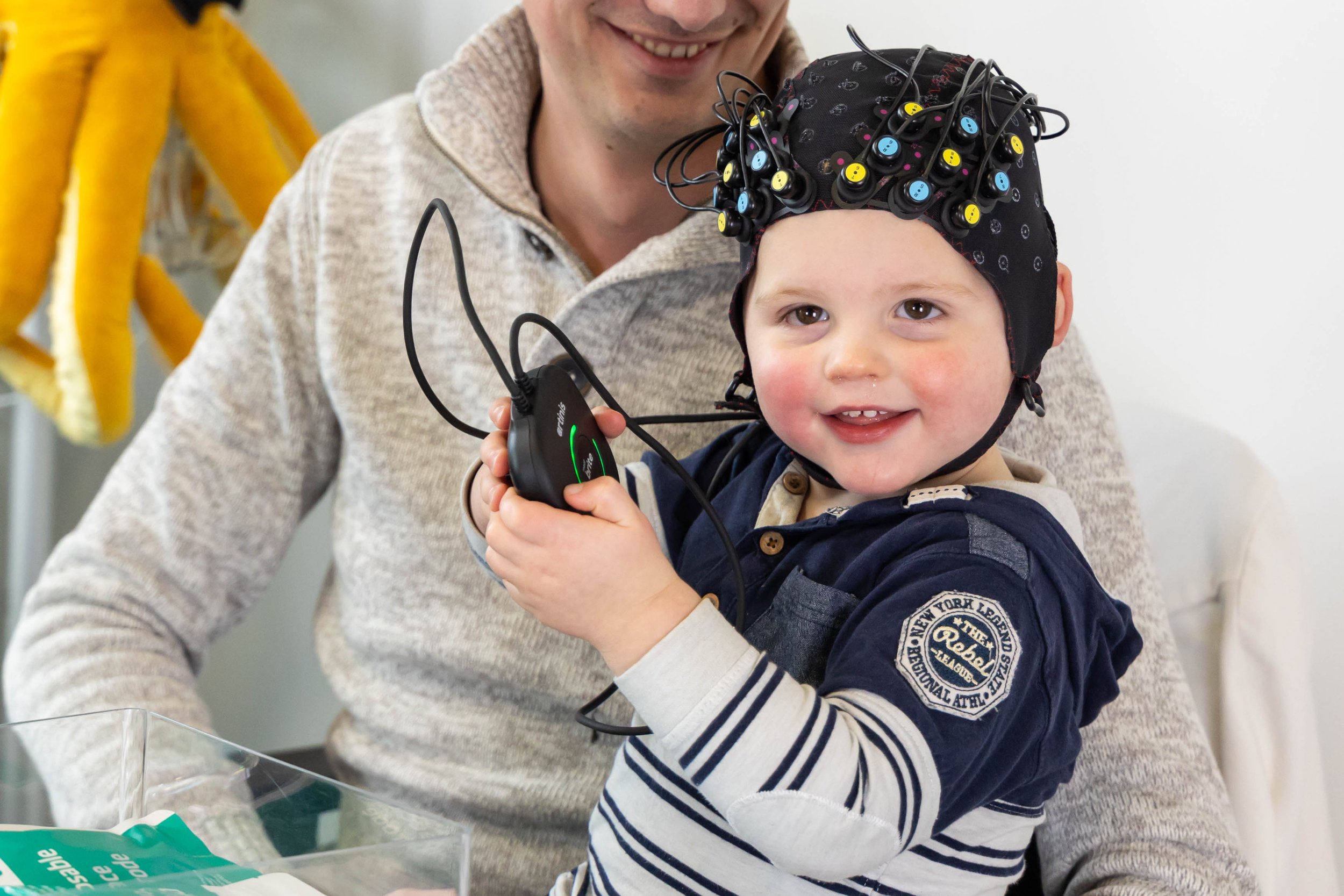
Especially when investigating (neural) development of toddlers, children, and adolescents, the performance of research in naturalistic settings can lead to novel insights and enhanced relevance in research regarding real-world behavior. Hence, fNIRS has become a popular tool to study the brain during social interaction, education, or other daily situations in children with normal and atypical development.
Study examples:
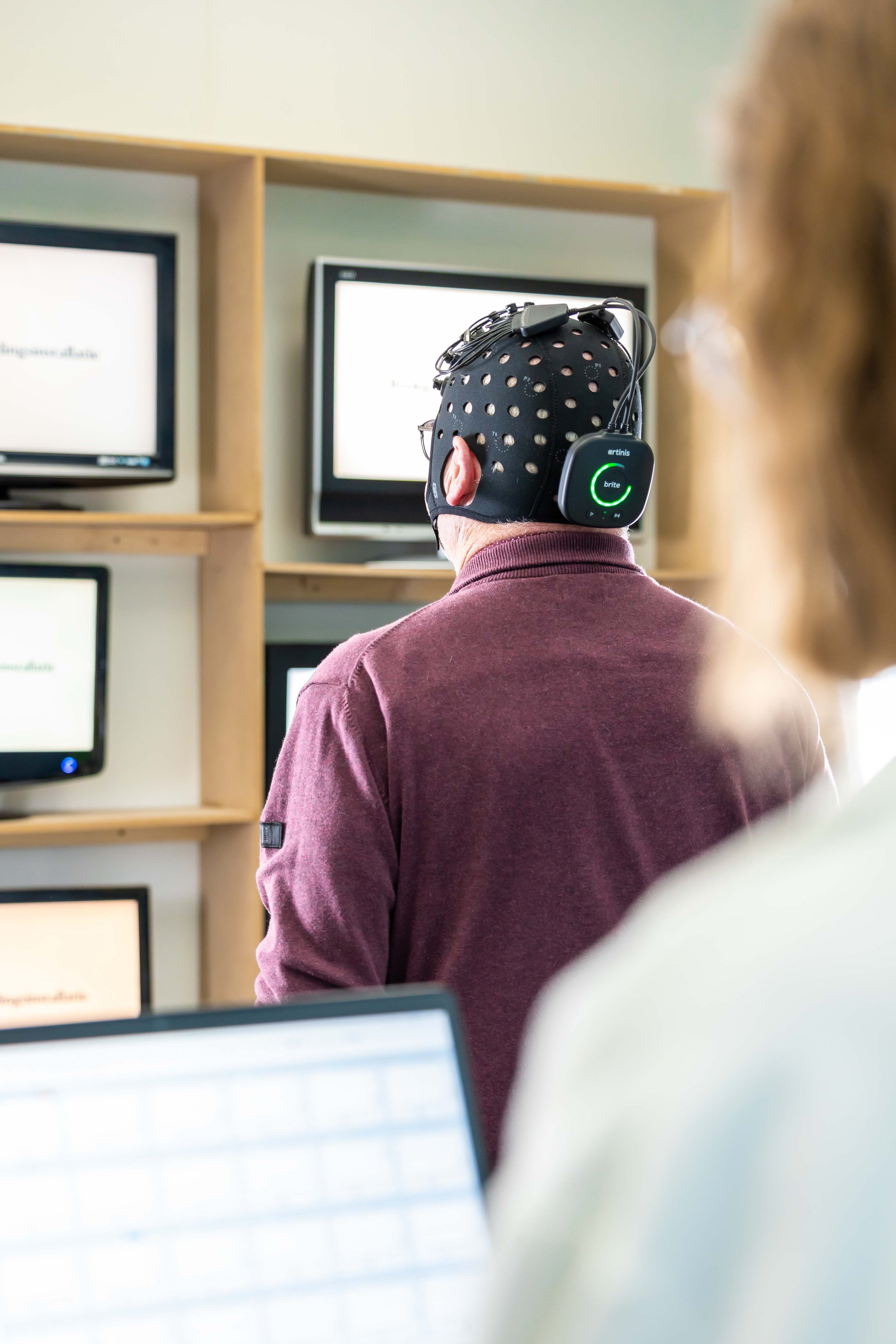
In a hyperscanning study performed by Feng et al., fNIRS was combined with machine learning to investigate neural mechanisms of real classroom teaching. Brain activity and interconnectivity of up to 16 students and one teacher were measured simultaneously using the Brite during blended teaching and lecturing alone. This study opens new doors in the world of fNIRS hyperscanning to study education in real classrooms.
Bulgarelli et al. created a unique real-world virtual reality setup and combined it with fNIRS to study the social interaction of preschoolers. Children played a bubble-popping game with different human-like avatars while brain activity was measured with a DualBrite. This research lays the foundation for the use of the latest technology and real-world scenarios to study social interaction in children and toddlers.
Artinis solutions:
At Artinis, we offer a range of devices that can be used to study the developing brain:
With its light weight and complete portability, the Brite can be comfortably used to measure brain activity from any cortical region in toddlers, children, and adolescents in various settings.
Our BabyBrite device is specifically designed for use in infants aged from 0 to 2 with extra comfort in mind.
The Brite Lite Frontal mini is the perfect fit to study prefrontal neural activity in toddlers and children.
Setting #2
Assessing the effect of sports and movement
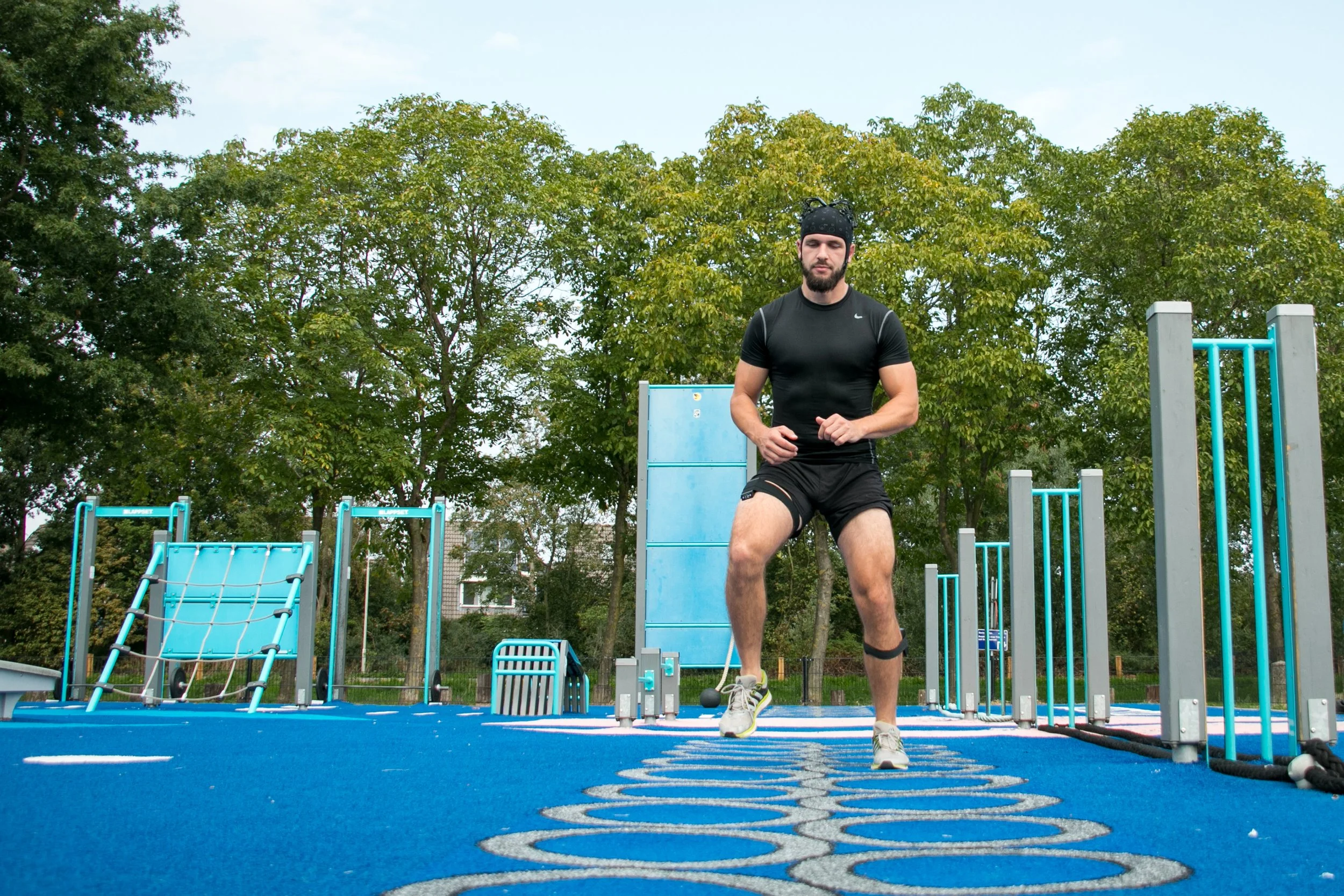
Studying brain activity during sports or movement can give valuable insights into decision-making and focus. Further, it can help to define cognitive load during demanding exercise or give information on fitness level. fNIRS is a perfect neuroimaging tool to perform research in the field during sports and exercise, as it is portable, easy to apply, and relatively insensitive to movement artifacts compared to other modalities.
Study examples:
Goodrick et al. used the Brite to study prefrontal brain activity before, during, and after performance of a 23-minute yoga asana session. Results identified inter-brain connectivity in frontal areas. This study overall showed the potential of fNIRS to provide new insights into brain activity in real-world scenarios involving movement.
At the University of Twente, Slutter and colleagues investigated the influence of the brain on anxiety during penalty kicks in experienced and less experienced soccer players using fNIRS. The Brite was used to measure brain activity while players performed penalty kicks under various conditions. This study laid the first foundation in proving the feasibility of using fNIRS in the field during physical activity.
What we offer at Artinis:
With our Brite family, we provide a group of devices offering complete portability, ease of use, and lightweight, while still including features that enable the achievement of high data quality even during motion and in outdoor settings, for instance, multi-power gain control and integrated ambient light protection. With the Brite and Brite Lite, it is possible to measure from any cortical region to assess, for instance, activity in frontal and/or motor areas. Our software solutions incorporate mechanisms to assess signal quality constantly, which enables monitoring of data quality even during movements.
Setting #3
Studying human well-being
Investigating human well-being is becoming increasingly important in the world of cognitive neuroscience. fNIRS can be used to measure cognitive load and better understand the neural mechanisms behind daily events that benefit wellbeing in naturalistic surroundings.
Study examples:
Dupuy et al. performed a study to investigate the potential association between prefrontal activity and psychological well-being during museum visits in elderly adults. Participants’ frontal activity was measured using the Brite during a 20-minute visit to an exhibition at the Montreal Museum of Fine Arts. The results indicated that the level of engagement during the analysis of artwork may influence the effect of a museum visit on anxiety.
The Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences built a brand-new laboratory to enable studying human health and wellbeing in real-world environments, focusing on wearable sensors, including, for instance, the Brite. The implementation of this so-called SENOLA lab, as well as methodological approaches and challenges to provide guidelines for research conducted in real-world labs, are discussed in this methodological paper.
What we offer at Artinis:
The prefrontal cortex is the brain region predominantly involved in processes of cognition and well-being. We provide a range of truly portable and comfortable fNIRS devices that are modified for easy and quick use in frontal brain areas:
Coming with a dedicated headband and template optimized for frontal areas, the Brite Frontal is perfect for measuring brain activity in the complete prefrontal cortex.
The Brite Lite Frontal comes with a specifically designed headband and can acquire frontal activity from 8 channels with a setup time of a few minutes.
Setting #4
Performing applied neuroscience research
In applied neurosciences, the performance of experiments in real-world settings is especially important. fNIRS can be highly customizable, which enables usage in uncommon and extreme settings, such as underwater or even in space.
Study examples:
D’Amario et al. assessed cardiac coherence of musicians performing in the Stavanger Symphony Orchestra and the Norwegian Radio Orchestra and selected audience members. Amongst others, the Brite was used to measure the brain activity of two violinists while playing. This study demonstrated the possibility of using fNIRS in naturalistic settings, connecting the fields of music and science.
Also in collaboration with the Stavanger Symphony Orchestra, Fagerland et al. performed a study to measure the brain activity of violinists during public concerts. Right temporal neural activation was acquired with the Brite and projected to the audience, and protocols for further analyses were developed in Brainstorm and Homer. Results demonstrated the feasibility of using fNIRS to assess brain activity related to producing arts in naturalistic settings.
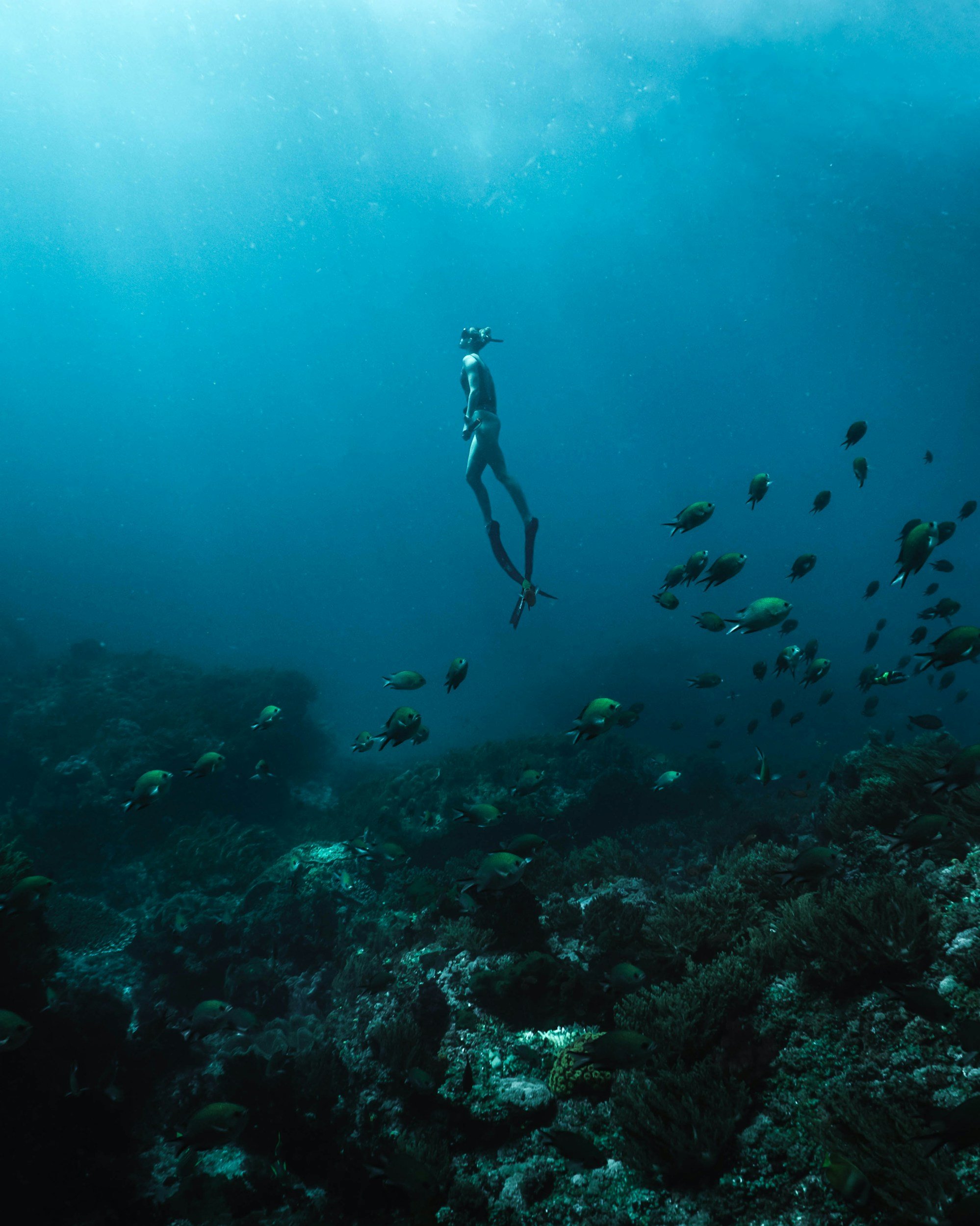
At Triton Systems, Inc., a customized Brite is used to measure brain activity during diving. Changes in brain activity in response to variations in breathing gas mixtures, cognitive load, and depths could be demonstrated. This research proves not only the versatility of fNIRS but also demonstrates its potential for use in extreme situations.
What we offer at Artinis:
The Brite is a highly versatile fNIRS device that provides almost no limits in terms of subject, measurement area, or experimental setting. It is perfect for use in applied sciences and proven to be applicable in various setups outside of the common lab.


![[PortaMon MKIII] crossfit-44.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/64e314a8c69b933a41187ec2/40deafdc-23cf-4565-a3f2-9b4c172b5ef9/%5BPortaMon+MKIII%5D+crossfit-44.jpg)










Although fNIRS is relatively insensitive for motion artefacts, they cannot be completely prevented. Fortunately, there are various ways to detect motion artefacts. In this second part of our blogpost series on motion artefacts, we explain different methods of detections and elaborate on their advantages and disadvantages.